Safety Rate
Safety Rate
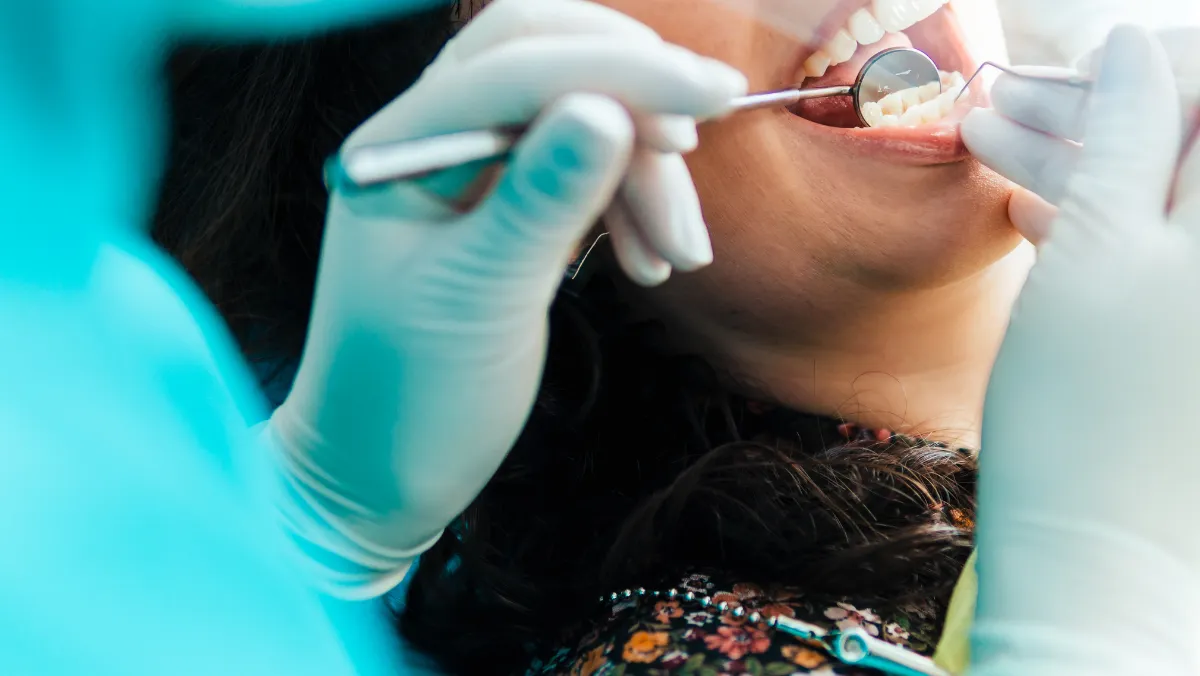
Subgingival curettage is a specialized dental procedure designed to remove diseased soft tissue from the inner surface of the periodontal pocket. This treatment plays a crucial role in controlling gum disease and preventing the progression of periodontitis, which is one of the leading causes of adult tooth loss worldwide. By targeting the inflamed tissue beneath the gum line, dentists aim to create a healthier environment that supports reattachment of the gums to the tooth surface.
The technique is typically performed after scaling and root planing when deeper tissue involvement is identified. Subgingival curettage is not considered a first-line treatment but rather an adjunctive therapy in cases of advanced gum conditions. It helps reduce pocket depth, minimize inflammation, and preserve natural teeth. Modern approaches emphasize minimally invasive methods that enhance patient comfort while improving long-term periodontal health and preventing further bone or tissue loss.
Subgingival curettage is a periodontal procedure that removes infected or inflamed tissue lining the gum pockets around the teeth. Unlike simple cleaning, this method targets the deeper areas beneath the gum surface, where bacteria and diseased tissue accumulate. The process involves using specialized curettes to gently scrape away the soft tissue, allowing the gums to heal and reattach more firmly to the tooth surface. This technique is often recommended for patients with moderate to severe periodontitis requiring focused treatment.
The main advantage of subgingival curettage is its ability to stop gum disease from progressing further into the supporting structures of the teeth. By removing inflamed tissue from the pocket lining, this procedure helps to reduce infection and restore a healthier gum environment. Patients often notice a significant reduction in swelling, bleeding, and tenderness following the treatment.
Key benefits include:
For many patients, subgingival curettage serves as a vital step in controlling chronic periodontal disease. It not only supports immediate healing but also contributes to the long-term stability of oral health. When paired with ongoing maintenance, the benefits of this treatment can be long lasting and transformative.
Post-treatment care is essential to ensure optimal healing and maintain the results of subgingival curettage. The gums will require time to recover, and proper aftercare minimizes discomfort while preventing reinfection. Patients are generally advised to follow specific routines for oral hygiene, diet, and activity levels.
Recommended practices include:
Adhering to these guidelines not only promotes faster healing but also reduces the risk of recurrence. By supporting tissue repair and maintaining a clean environment, patients give their gums the best chance of long-term recovery and improved stability.
Like all dental procedures, subgingival curettage carries potential risks, although complications are generally uncommon when performed by an experienced professional. Understanding these risks helps patients make informed decisions and prepares them for the recovery process.
Possible risks include:
Overall, the benefits of subgingival curettage generally outweigh these risks, particularly in patients suffering from persistent gum disease. Clear communication with the dentist, combined with diligent home care, ensures that complications are minimized. When performed under proper clinical conditions, this procedure remains a safe and effective approach to periodontal therapy.
Subgingival curettage is typically recommended when standard scaling and root planing have not sufficiently resolved gum inflammation or pocket depth. It is indicated in cases of chronic or advanced periodontitis where diseased tissue remains in the inner lining of the gums. Patients who experience persistent bleeding, deep periodontal pockets, and attachment loss often benefit from this approach.
Indications include:
Contraindications include:
By carefully evaluating each patient’s condition, dental professionals can determine whether subgingival curettage is appropriate. It is not a universal treatment but rather a targeted solution for specific periodontal challenges. Proper case selection ensures that patients achieve the best possible results while avoiding unnecessary interventions.
Subgingival curettage can be classified into different types based on the technique and instruments used. Each method has specific indications depending on the severity of disease and the desired clinical outcome.
Types include:
The choice of method depends on the depth of periodontal pockets, patient tolerance, and the dentist’s expertise. While traditional manual curettage remains widely practiced, advancements like laser therapy have improved accuracy and patient comfort. Each technique ultimately aims to restore gum health by eliminating diseased tissue and promoting reattachment. A tailored approach ensures optimal results for individual periodontal needs.
Maintaining the benefits of subgingival curettage requires a combination of professional follow-ups and diligent home care. The procedure is only the first step; long-term success depends on how well patients sustain their oral hygiene habits.
Effective maintenance strategies include:
By integrating these practices, patients can protect the improvements gained from subgingival curettage and reduce the likelihood of disease recurrence. Maintenance is not only about protecting gums but also about preserving overall oral function and confidence in one’s smile. Consistency and professional guidance are key to ensuring lasting periodontal stability.
Subgingival curettage is a valuable periodontal therapy aimed at removing diseased tissue, reducing pocket depth, and restoring gum health. Although it is not the first step in treating gum disease, it plays an important role in cases where conventional cleaning alone cannot address deeper tissue involvement. The procedure offers long-term benefits such as improved gum attachment, preservation of natural teeth, and prevention of disease progression.
Like any dental treatment, subgingival curettage requires careful case selection and dedicated aftercare to achieve the best outcomes. With advancements in techniques and instruments, the procedure has become safer and more comfortable for patients. Consistent oral hygiene, lifestyle choices, and regular dental visits further enhance its effectiveness. When performed under the guidance of a skilled professional, subgingival curettage remains a cornerstone therapy in maintaining healthy gums and supporting a lifetime of strong, functional teeth.
A subgingival curette is a specialized dental instrument designed to clean beneath the gum line. It is used to remove soft tissue and bacterial deposits from periodontal pockets where standard cleaning tools cannot reach. By eliminating diseased tissue and reducing bacterial load, the curette plays a critical role in controlling gum disease, improving gum health, and promoting reattachment of the gums to the tooth surface.
The purpose of dental curettage is to eliminate inflamed or infected gum tissue that contributes to periodontal disease. By scraping away diseased lining from inside the periodontal pocket, the procedure reduces inflammation and encourages healthy gum reattachment. This helps lower the depth of the pocket, prevents further damage to supporting structures, and preserves natural teeth. Dental curettage serves as both a therapeutic and preventive measure in advanced gum care.
Subgingival scaling aims to remove hardened plaque and calculus deposits that accumulate below the gum line. These deposits harbor harmful bacteria, which trigger inflammation and tissue destruction if left untreated. The procedure smooths the root surface, discourages bacterial colonization, and allows the gums to heal properly. Subgingival scaling is often performed before or alongside curettage to maximize periodontal health and support long-term stability of the teeth.
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort