Safety Rate
Safety Rate
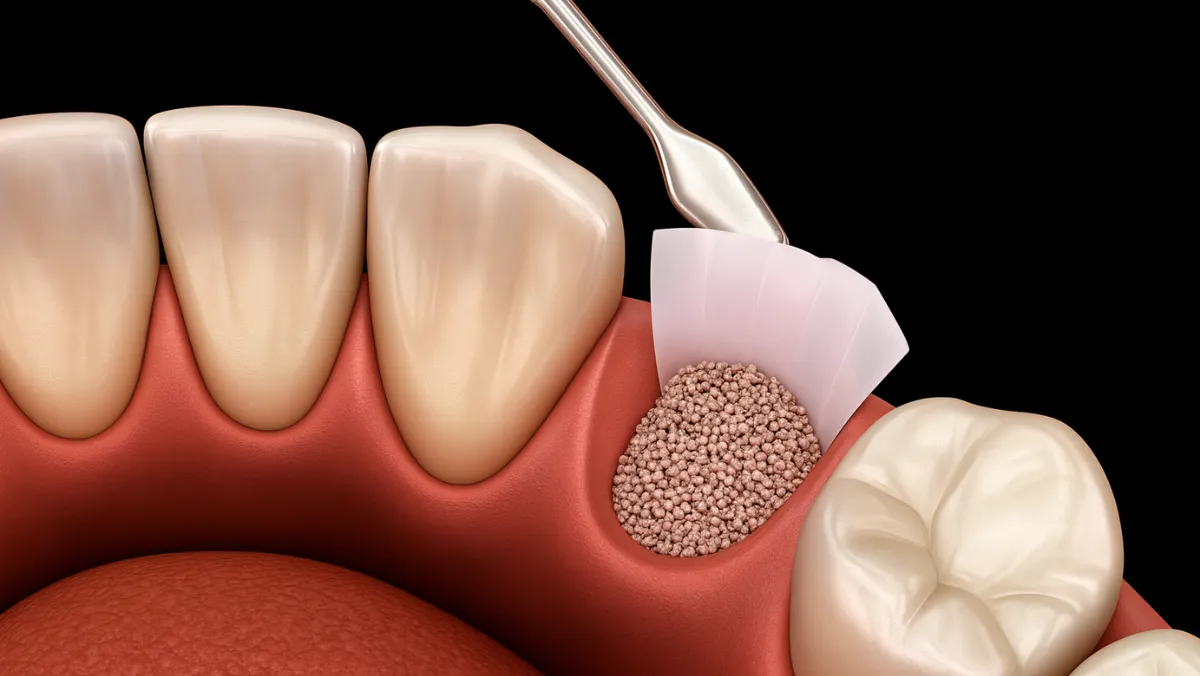
Bone grafting is a specialized surgical procedure that helps restore or regenerate bone tissue in areas where it is missing, damaged, or weakened. Surgeons often use this technique when the body needs additional support for bone healing, whether from trauma, disease, or structural deformities. It plays a crucial role in dentistry, orthopedics, and reconstructive surgeries, making it a cornerstone for successful medical outcomes.
The graft can be taken from the patient’s own body (autograft), a donor source (allograft), or even created synthetically using biocompatible materials. Each method is carefully chosen based on the patient’s condition and the intended surgical results. Studies show that bone grafting significantly improves healing outcomes, particularly in complex fractures and implant procedures.
By filling bone voids and stimulating natural regeneration, bone grafting not only restores physical function but also enhances overall quality of life for patients dealing with bone-related complications.
Bone grafting is recommended when natural healing is not enough to restore bone strength or structure.
The type of graft depends on medical needs, the source of bone, and the desired outcome.
The surgical process is designed to be precise and minimally invasive whenever possible.
Though considered safe, bone grafting carries potential complications like any surgical procedure.
The advantages often outweigh the risks, especially for long-term outcomes.
Recovery is carefully monitored to ensure graft integration and healing.
Long-term outcomes are highly positive when patients follow recovery guidelines.
Prevention and preparation play a major role in graft success.
Bone grafting is a vital medical procedure that restores structural integrity, enhances healing, and improves long-term health outcomes. Whether used in dental treatments, trauma care, or spinal surgeries, the procedure provides a reliable way to rebuild and regenerate bone where natural recovery falls short. With advancements in surgical methods and materials, the success rate of bone grafting continues to rise, offering patients lasting stability and function.
By strengthening bone foundations, the procedure not only supports implants and repairs fractures but also restores quality of life through improved movement, confidence, and comfort. While the process involves certain risks, careful planning and adherence to medical guidance significantly reduce complications.
If you are facing bone loss, injury, or preparing for reconstructive treatment, bone grafting may be the solution to restore both form and function. Consulting with a specialist ensures the best approach tailored to your unique needs.
Pain levels after bone grafting vary depending on the procedure type and location. Most patients report mild to moderate discomfort, which is manageable with prescribed pain relievers. In dental cases, soreness usually subsides within a week, while orthopedic grafts may require longer recovery. Swelling and bruising are expected but temporary. With modern anesthesia techniques and post-operative care, the procedure is well-tolerated, and most patients return to normal routines with minimal disruption after the healing phase begins.
Yes, bone grafting encourages natural regeneration by acting as a scaffold for new tissue. Over time, the graft material fuses with the patient’s existing bone, allowing cells to grow and strengthen the area. This process can take several months, depending on the graft type and the patient’s overall health. Once integrated, the grafted bone behaves like natural bone, providing lasting stability and support for implants, joints, or structural repairs in the treated region.
Meet our experienced team of anaesthesiologists dedicated to your safety and comfort
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort