Safety Rate
Safety Rate
Mobile tooth treatment addresses the condition where teeth lose their firmness and begin to shift within the socket. This issue is often linked to weakened supporting structures, such as the gums and jawbone, and requires timely attention to prevent tooth loss. While minor movement in children’s teeth is normal due to natural shedding, mobility in adult teeth is typically a sign of underlying dental or periodontal problems. Left untreated, it can affect chewing, speech, and overall oral health.
Modern dentistry provides several effective methods to restore stability, including scaling, splinting, root canal procedures, and in severe cases, surgical intervention. Early detection not only preserves teeth but also prevents associated complications, such as gum disease and bone resorption. Addressing mobility through professional dental care significantly improves oral function, aesthetics, and long-term dental health.
Tooth mobility refers to the abnormal movement of a tooth within its socket when pressure is applied. In healthy conditions, teeth have minimal flexibility due to the periodontal ligament, but noticeable looseness indicates weakening of supporting structures. This condition can arise from gum disease, trauma, or bone loss. Tooth mobility should never be ignored, as it can progress to tooth loss if untreated. Proper diagnosis and timely management play a crucial role in maintaining dental function and preventing further complications.
Adult teeth are designed to last a lifetime, supported firmly by gums, ligaments, and jawbone. When these supporting structures weaken, teeth may loosen and become mobile. Unlike children, where mobility is natural due to exfoliation of baby teeth, adults experience this issue due to underlying conditions.
Neglecting mobility can lead to progressive tooth loss, impaired chewing, and speech difficulties. Timely consultation with a dentist allows for diagnosis and appropriate treatment, ranging from deep cleaning to splinting or surgical interventions. Maintaining good oral hygiene and addressing health conditions promptly reduces the chances of mobility in adult teeth.
There are several contributing factors behind tooth mobility, many of which relate to gum and bone health. Understanding these causes is key to effective treatment.
Identifying the exact cause through professional examination is essential to determine the right treatment. Neglecting these causes accelerates damage, increasing the risk of irreversible tooth loss.
Recognizing symptoms of tooth mobility helps in seeking early treatment. While minor signs may seem harmless, they often indicate a developing issue.
Ignoring these symptoms may allow the problem to worsen, leading to loss of teeth and damage to surrounding bone. A dental professional can evaluate these signs with clinical examination and imaging to provide an accurate diagnosis and timely intervention.
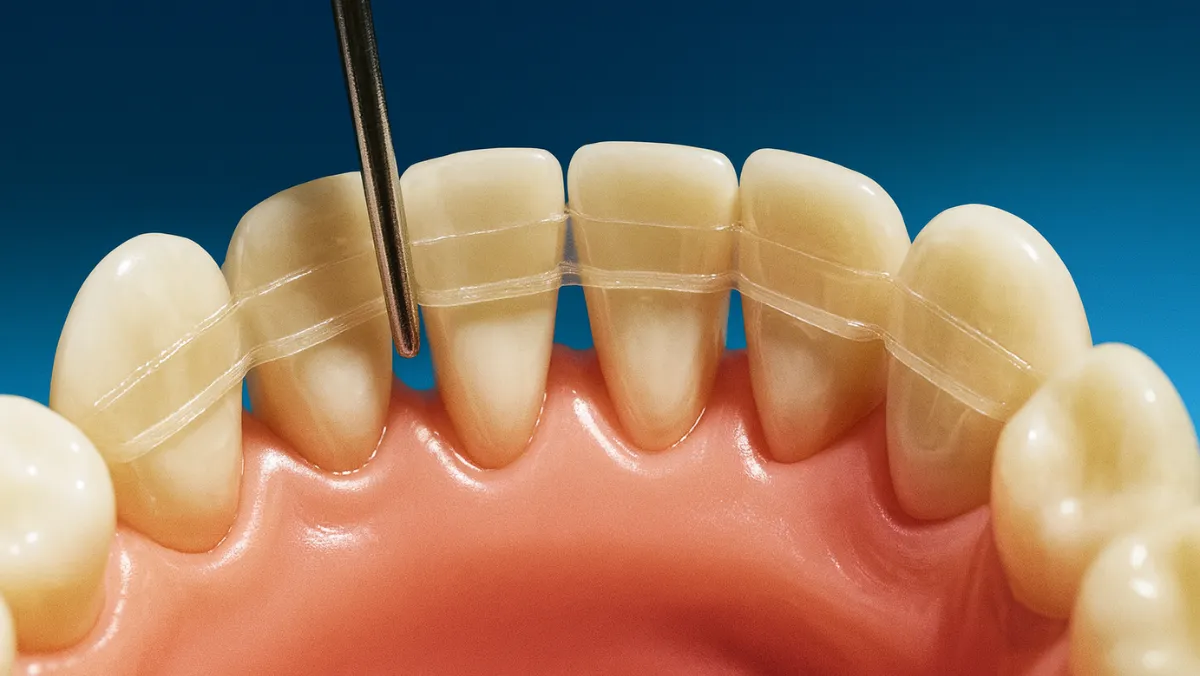
Treatment for mobile teeth depends on the severity and underlying cause. Early intervention increases the chance of saving the natural tooth.
Dentists often combine treatments with lifestyle advice such as improving oral hygiene, quitting smoking, and managing systemic conditions. With proper care, many mobile teeth can be stabilized and preserved.
Preventing tooth mobility requires consistent oral care and awareness of habits that may damage supporting structures.
Simple preventive measures go a long way in maintaining dental stability and overall oral health. By combining personal care with professional supervision, one can significantly reduce the risk of developing mobile teeth.
Mobile tooth treatment is crucial in preserving natural teeth and ensuring overall oral health. Early detection of mobility prevents complications such as gum recession, bone loss, and eventual tooth loss. With advancements in dentistry, effective treatment options like scaling, splinting, and regenerative procedures can restore stability and improve function. Maintaining consistent oral hygiene, addressing systemic conditions, and avoiding harmful habits significantly reduces the likelihood of tooth mobility.
Taking proactive steps not only safeguards the health of individual teeth but also preserves the harmony of the entire dental structure. Professional dental guidance ensures that mobility is addressed at its root cause, offering long-term solutions. Timely treatment not only restores confidence in chewing and speaking but also enhances overall well-being. Prioritizing preventive care and early intervention is the key to maintaining strong, stable, and healthy teeth for life.
Yes, mobile teeth can often be saved if treatment begins early. Depending on the cause, procedures such as scaling, splinting, or root canal therapy may stabilize the tooth. In cases of gum disease, controlling infection and improving bone support are crucial. With proper care and regular dental supervision, many patients can retain their natural teeth without requiring extraction.
Root canal treatment can be performed on a mobile tooth if the looseness is due to infection inside the pulp. However, if mobility is primarily caused by severe bone loss or gum disease, RCT alone may not be sufficient. Dentists usually combine endodontic procedures with splinting or gum treatments to improve stability and save the affected tooth.
A mobile tooth means the supporting structures such as gums, ligaments, or jawbone are weakened. It can be caused by gum disease, trauma, or infection. While slight natural movement is normal, noticeable looseness in adult teeth signals an underlying issue. Immediate dental evaluation is important to prevent further damage and to decide the best course of treatment.
Root canal treatment is not typically performed without anesthesia because the procedure involves removing infected tissue from inside the tooth, which can be very painful. Local anesthesia ensures the process is comfortable and stress-free for the patient. Modern techniques and numbing agents make RCT almost painless, improving patient experience and ensuring precise treatment without discomfort.
The cost of root canal treatment varies depending on the tooth involved, severity of infection, and additional procedures required. Molars are generally more expensive due to their complex anatomy. Other factors include the clinic location and dentist’s expertise. Although costs can seem significant, RCT is a cost-effective way to save natural teeth compared to tooth extraction and replacement options.
Our experienced anaesthesiologists are here to ensure your safety and comfort